All Indian citizen are required to pay a percentage of their income to the government who uses this income towards infrastructural and economic development. Although, income tax return payment and rates are related to government approved laws and it follows the Income Tax Act, 1961. It falls under the direct taxation category and it is the biggest revenue generator for the government. Central Board of Direct Taxes or CBDT has been assigned to take care of this type of tax collection.
Each and every Indian individual person, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), local authorities, Association of Persons (AOP), companies, corporate firms, Body of Individuals (BOI), and all other artificial juridical persons who earn over the non-taxable bracket are responsible for paying income tax return. Income tax is collected on the basis of annual income and the cycle of income tax run from 1st April to 31st March. The years are classified as Financial Year and Assesment Year as described by the law. The income year is called Financial Year and the year when the income is charged is called Assessment year.
The tax collection is done in three ways in India
Get the detail process of ITR Verification to Income Tax Department Get Details
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2017-18
Tax slabs are different for different taxpayer categories depending on their annual income.
For the current financial year 2017-18 are as follows
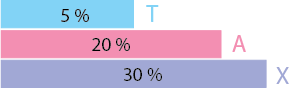
Income tax slab for individual tax payers & HUF (less than 60 years old) (both men & women)
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 2,50,000* |
No Tax |
| INR 2,50,000 – INR 5,00,000 |
5% |
| INR 5,00,000 – INR 10,00,000 |
20% |
| Above INR 10,00,000 |
30% |
|
Surcharge:
- 10% of income tax, where total income is between INR 50 lakhs and INR 1 crore.
- 15% of income tax, where total income exceeds INR 1 crore.
|
| Cess: 3% on total of income tax + surcharge. |
| * Income upto INR 2,50,000 is exempt from tax for individuals with age 60 years or less. |
Income tax slab for individual tax payers & HUF (60 years old or more but less than 80 years old) (both men & women)
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 3,00,000* |
No Tax |
| From INR 3,00,000 – INR 5,00,000 |
5% |
| From INR 5,00,000 – INR 10,00,000 |
20% |
| Above INR 10,00,000 |
30% |
|
Surcharge:
- 10% of income tax, where total income is between INR 50 lakhs and INR 1 crore.
- 15% of income tax, where total income exceeds INR 1 crore.
|
| Cess: 3% on total of income tax + surcharge. |
| * Income up to INR 5,00,000 is exempt from tax if you are more than 80 years old. |
Income tax slab for super senior citizens (80 years old or more) (both men & women)
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 2,50,000* |
No Tax |
| Up to INR 5,00,000 |
No Tax |
| From INR 5,00,000 – INR 10,00,000 |
20% |
| Above INR 10,00,000 |
30% |
|
Surcharge:
- 10% of income tax, where total income is between INR 50 lakhs and INR 1 crore.
- 15% of income tax, where total income exceeds INR 1 crore.
|
| Cess: 3% on total of income tax + surcharge. |
| * Income up to INR 5,00,000 is exempt from tax if you are more than 80 years old. |
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2016-17
Income Tax Slab for Individuals and Hindu Undivided Families
These tax slabs are applicable for income tax return filing the previous Financial Years 2016-17 (AY 2017-18), 2015-16 (AY 2016-17), 2014-15 (AY 2015-16). An Education Cess of 2% and SHEC of 1% will be levied on the tax calculated with the information given in below tables given below.
Income Tax Slab for male/female individuals up to 60 years of age and HUFs
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 2,50,000 |
No Tax |
| From INR 2,50,000 to INR 5,00,000 |
5% exceeding INR 2,50,000 |
| From INR 5,00,000 to INR10,00,000. |
20% exceeding INR 5,00,000 |
| Above 10,00,000 |
30% exceeding INR 10,00,000 |
Income Tax Slab for all individuals above 60 years of age (Senior Citizens)
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 3,00,000 |
No Tax |
| From INR 3,00,000 to INR 5,00,000 |
10% exceeding INR 3,00,000 |
| INR 5,00,001 - INR 10,00, 000 |
20% exceeding INR 5,00,000 |
| Above INR 10,00,000 |
30% exceeding INR 10,00,000. |
Income Tax Slab for all individuals above 80 years of age (Super Senior Citizens)
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 5,00,000 |
No tax |
| From INR 5,00,000 to INR 10,00,000 |
20% exceeding INR 5,00,000 |
| Above INR 10,00,000 |
30% exceeding INR 10,00,000 |
Income Tax Slab for Business Firms, Local Authorities, Corporates and Domestic Companies
For these entities, income tax is imposed at a rate of 30% on the total declared income along with an applicable surcharge of 5% on the total tax amount if the domestic companies earn above Rs.1 Cr. However, this surcharge is not applicable on firms and local authorities.
Income Tax Slab for Co-operative societies
| Income Tax Slab |
Tax Rate |
| Up to INR 10,000 |
10% |
| From INR 10,000 to INR 20,000 |
20% exceeding INR 10,000 |
| Above INR 20,000 |
30% exceeding INR 20,000 |
| Forms |
Description |
| ITR 1 (SAHAJ) |
For Individuals having Income from Salary & Interest. |
| ITR 2 |
For Individuals & HUFs not having Income from Business or Profession |
| ITR 2A |
For Individuals & HUFs not having Income from Business or Profession and Capital Gains and who do not hold foreign assets |
| ITR 3 |
For Individuals/HUFs being partners in firms and not carrying out business or profession under any proprietorship |
| ITR 4 |
For Individuals & HUFs having income from a proprietary business or profession |
| ITR 4S (SUGAM) |
For Individuals/HUF/Partnership Firm having income from presumptive business |
| ITR 5 |
For persons other than,- (i) individual, (ii) HUF, (iii) company and (iv) person filing ITR-7 |
| ITR 6 |
For Companies other than companies claiming exemption under section 11 |
| ITR 7 |
For persons including companies required to furnish return under sections 139(4A) or 139(4B) or 139(4C) or 139(4D) or 139(4E) or 139(4F) |
These forms can be downloaded from the official website or our website for the current Assessment year and last 2 financial year.
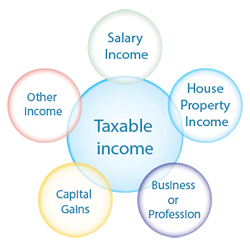
Types of taxable income
All income are taxable in income and these income are mentioned in different heads of the income tax return filing form
Salary Income
All the income salaried employees receive from their employer is referred as salary income and needs to be mentioned under “income from salaries” head. Employers are bound to make deductions for the employees falling under taxable slabs and produce Form 16 with mentioning all the deduction and paid income details in it.
House Property Income
If the taxpayer has a let out house property then income received from that will be taxable under the “Income from House Property” tab. If the taxpayer and their family is residing in that house then it will be counted as a “Self-occupied property” which is exempted from any tax liabilities.
House Rent Allowance Summary and its Advantages Get Details
House property income is calculated as given below
Gross Annual Value (GAV) = 10
Less: Municipal Taxes Paid = 3
Net Annual Value = 10-3
Less: Deductions under Section 24 = 2
Income from House Property = (10-3) – 2
Profits and Gains from Business or Profession
Any income made from business or professional services are taxable and tax will be calculated as mentioned under section 30 to 43D.
Capital Gains
Any assets held by the taxpayer such as land, building, bonds, equity shares, debentures, arts, jewellery and other assets are considered as capital gain and any income made from these sources need to be declared under “Income from Capital Gains” head.
Other income: Income from Other Sources
Any income that is not listed under the above souces need to be mentioned under the “Income from Other Sources” head.
The income falling under these headings include
- Income made from dividends.
- Horse race or lottery winnings
- Gifts recived from anyone other than blood relations
- Any rental income except house property
- Interest earned on debentures, government securities, and bonds etc
- Family pension
- Interest earned from anything except securities
- Interest received on any compensation
- Employee’s contribution towards staff welfare schemes, any fund set up under the ESIC Act that’s received by the employer from the employees.
Deductions
There are many deductions can be applied on total taxable income during income tax online filing, if the taxpayer have invested a sum of money into prescribed plan:
Section 80C
If taxpayer have done investment on NSCs or certain scheme than they can avail deduction up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs.
Section 80CCC
Upto Rs. 1.5 lakhs deduction can be availed against payment made to LIC or any pension scheme.
Section 80CCD
Maximum 10% of the salary amount can be deducted from taxable income against investment made into New Pension Scheme. However, the limit is not up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs as it is prescribed for the above two sections.
Section 80D
This section allow deduction against health insurance scheme. Up to Rs.2 lakhs deduction can be claimed under this section by an individual or HUFs.
Section 80DDB
Deduction can be claimed against treatment expense of a disease prescribed under the rules (11DD) for a family member or a member of HUFs.
Section 80E
Deductiosn can be claimed against interest paid on education loan taken for self or blood relations to take education in India.
Section 80EE
The first time home owners can claim deduction under this section for a home bought in a value less than 40 lakhs and a loan of 25 lakhs or below has bene taken for the same.
Section 80RRB
Deduction up to Rs.3 lakhs can be claimed against income made from royalty or patents under this section.
Section 80TTA
Deduction up to Rs.10,000 can be claimed against interest earned from savings account with a bank/post office/co-operative societies.
Section 80U
Disable person can claim a deduction up to Rs.1,00,000 by producing their disability certificate and the amount depends on the severity of the disability.
Section 24
Deduction up to Rs.2 lakhs can be claimed per year against interest paid on home loans tact is tax exempt.
Find more detail of All about Deductions under Section 80 Get Details
TDS or Taxes Deducted at Source
Employers deduct some amount from employee’s salary before distributing it as prescribed by the government law. Employer later submit this amount to the government. However, this deduction is not applicable for income group below Rs.2,5 lakhs for individuals, Rs.3 lakhs for senior citizens and Rs.5 lakhs for super senior citizens.
Find more about TDS
In India, people can also do income tax online filing, TDS e-filing or other tax e-filing either through government income tax website or through registered intermediary websites. Its more faster than paper filing and for certain groups, it I s mandatory to file income tax return online.
 Tax
Tax
 Income Tax
Income Tax
 Sales Tax
Sales Tax
 TDS
TDS
 GST
GST
 Service Tax
Service Tax
 VAT
VAT
 Tax Calculator
Tax Calculator