A Complete Guidelines Explaining Goods and Services Tax
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is soon going to land soon in Indian tax system by July 2017. This system will amend all the current indirect taxation system and will bind all goods and services under one taxation umbrella. This page will give you a brief overview of this new tax reformation.
Introduction to GST
Goods and Services Tax or GST is a destination oriented consumption tax system that will be levied on goods and services provided in India. This tax will be imposed on each stage of goods manufacture and distribution and input taxes will be set-off against output taxes. It will be a comprehensive and integrated tax system levied on value addition at each stage.
Get complete assistance required for GST registration Get Solutions
Currently, India has a number of indirect taxation system by which both state and central government collect the tax which ultimately imposes double-tax on many goods and services. This system will subsume all these indirect taxes and will bring a stability in tax revenue system of India. An improved tax compliance will be built by this system which can be seen in 150 other developed countries who uses it from last many decades.
The Salient Features
Part 1: Dual Model
- Although it is proposed to be a uniform model for all India but it will have different model specified for states and center. They will be identified as State GST (SGST) and Central GST (CGST).
- These different models will share the same definition of a taxable event and taxable person, chargeability, measure of levied tax, valuation provisions, the basis of classification etc.
- The SGST will be collected by state Government and CGST will be collected by Central Government.
- This model will maintain the constitutional requirement of Fiscal federalism for the states and center as it is defined for federal India.
Part 2: Single Integrated Comprehensive indirect tax:
- Many of the current indirect taxation systems will be subsumed under this integrated taxation system called Goods and Services Tax.
-
The central taxes which will be subsumed are:
- Central Excise duty
- Special Additional duties of customs.
- Countervailing duties (CVD)
- Various cesses and surcharges
- In place of these Central taxes, CGST will be levied on the service and goods
-
The state taxes which will be subsumed are:
- VAT or Value Added Tax
- Entry tax
- Luxury tax
- Entertainment tax,
- Tax on the lottery, betting, and gambling
- In place of these State taxes, SGST will be levied on the service and goods.
Registration, Audit, and Documents Required for GST Procedure Get Details
Part 3: Destination based consumption tax
The tax levied on goods and services will be added to the revenue of the place where it will be consumed.
For instance, if a seller of Haryana sells a good or service to a seller of Uttar Pradesh, then the tax will be credited to UP Government along with Central Government.
Getting GST Enrolled
Any Existing taxpayers enrolled under Central Excise, Customs, Service Tax, VAT and Sales Tax are required to get enrolled with GST system.
The GST enrollment needs to be done online through the GST system portal. Businesses with an annual turnover above 20 lakhs need to be registered with this system. However, the limit is l0 lakhs for the north-eastern states. To get registered, a taxpayer needs to get the provisional ID and password from the concerned state authorities to access the GST system portal.
Documents required to get registered under GST system are:
-
For the taxpayer:
- Provisional ID
- Password
- Valid personal email address
- Valid mobile number
- Bank account number
- IFSC code
-
Documents required to be uploaded to the website:
- Photograph of promoters / partners / Karta of HUF (JPEG file not exceeding 100 KB in size).
- Proof of business constitution such as partnership deed or business registration certification of the entity (PDF or JPEG file not exceeding 1 MB in size).
- Proof of appointment of authorized signatory (PDF or JPEG file not exceeding 1 MB in size).
- Photograph of authorized signatory (JPEG file not exceeding 100 KB in size).
- The front page of bank passbook / statement which contains the details including bank account number, branch address, account holder’s address and few current transactions.
Filing GST Return
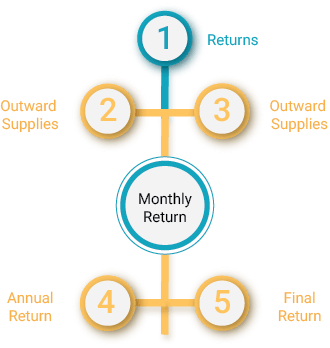
Types of GST Return:-
- Outward: GSTR-1 need to filed by 10th of succeeding month as levied u / s-8 / TDS u / s-37 and this applies to every registered entity or person except Input Service Distributor (ISD).
- Inward: GSTR-2 need to be filed by the person who will not file GSTR-1 need to file this by 15th of succeeding month.
-
Monthly:
GSTR-3 need to filed by 20th of succeeding month as levied u / s-8 / TDS u / s-37 except for Input Service Distributor (ISD).
GSTR-4 need to be filed in quarterly basis by the compounding taxpayer u / s 8 by 18th of the month next to a quarter.
GSTR-5 need to file by the NRFs periodically by last day of registration.
GSTR-6 need to filed by Input Service Distributors (ISD) by 15th of the next month.
GSTR-7 need to file to submit the return collected for Tax Deducted at Source u / s 37 by 10th of the next month.
- Annual Return: GSTR-8 need to be filed annually 31st December following the end of the financial year.
- Final Return:If any taxpayer or entity decide to cancel the registration, then they need to file a final return with 3months of the date of cancellation or date of cancellation order.
The Advantages of GST for Citizens and for the Economy Get Details
Matching Concept:
In this Goods and Services Tax, return filed by the inward and outward seller will be matched with each other. Both the parties need to keep their invoice updated in the portal to avail credit.
- First, GSTR-1 will be filed by the outward seller 10th of the succeeding month.
- Then the inward person filing a GSTR-2 need to verify the details which were filed with GST1 by the outward seller.
- If the detail does not match for reversal and reclaims of input credit, then the defaulter will have to pay additional tax with interests.
- No such rectification can be done after filing the annual return or final return whichever is earlier.
Different types of Ledger:
- ITC Ledger of taxpayer continuous
- Cash Ledger of taxpayer continuous
- Tax Ledger of taxpayer continuous
Important Points:
- A registered taxpayer is not allowed to file monthly Goods and Services Tax return unless he / she have not filed the return for the previous month.
- The penalty has been prescribed for filing a late return for the registered taxpayers.
- Late filing of GSTR - 1/2 or final return will result in a late fee of INR 100 per day from the default payment date and the maximum penalty can be INR 5000.
- Late filing of GSTR-8 will result in a late fee of INR 100 per day from the default payment date and the maximum penalty can be ¼% of aggregate turnover.
- GST system will have minimal chances for late filing as it will provide a regular update for claiming credit.
Read More About
More about Goods and Services Tax
Applicable GST Rate:
The final decision for GST rates have not been decided yet and it is still under revision. It has been assumed that rates will be different for CGST, SGST, and IGST and there may be multiple rates for goods and services depending on their importance. In brief, taxes will be lower for essential goods and will be higher for luxury goods.
Simultaneous taxation under CGST and SGST for Inter-State transaction:
For the inter-state transaction of goods and services, the tax levied will be Integrated Goods and Service Tax (IGST) which is a total of CGST and SGST. This will be applicable while selling goods to the buyer from other states and this IGST will be payable only after adjusting the available credit of IGST+CGST+SGST paid on buying the goods. The selling state is supposed to transfer the credit to SGST and the buyer can claim credit for the IGST during discharging SGST liabilities. And the center will transfer the credit of IGST used in payment of SGST to buyer’s state.
Simultaneous taxation under CGST and SGST for Intra-State transaction:
For the transaction of goods and services within the state will levy SGST and CGST on them. The payment for SGST will be done only by SGST credit and CGST will be done by CGST credits. No cross adjustment will be allowed in such cases.
People Also Searched For
 Tax Glossary
Tax Glossary





