An Overview of Direct and Indirect Taxes in India
Taxes are basically referred to the obligatory fees imposed upon the earnings of corporations and individuals by the government for financing the nation’s developmental schemes. There are primarily two types of taxes; namely Direct Tax and Indirect Tax.
Direct and indirect taxes comprise of all the various forms of taxes charged by the government. Direct taxes are the taxes which taxpayers pay directly to the government and it cannot be shifted to another individual. Taxpayers who earn a taxable income are required to pay a percentage of their earnings to the government.
A Simple Explanation of Income Declaration Scheme Get Details
While on the other hand, Indirect Taxes are the Value Added Tax (VAT) that comes along with the bills, for the goods and services which you have obtained from the seller or the provider. Indirect Taxes are transferable. When manufacturers or service providers are levied with an initial tax, they can shift the burden of tax payment to the consumer. A result of which, consumers are charged a higher price for the commodity as the taxes come added with the bill.
Direct and indirect taxes are both fundamental components that add to the revenue earned by the Indian government which is utilized for any developmental initiatives by the government.
What are the Reasons Behind Taxation by the Government?
The obvious reason behind the imposition of taxes is because they are the primary source of revenue earned by the government. These revenues can be utilized by the government for expenditures on defense system, healthcare facilities, providing education, building different infrastructure facilities like the construction of roads, dams, highways etc.
Understanding the Two forms of taxes
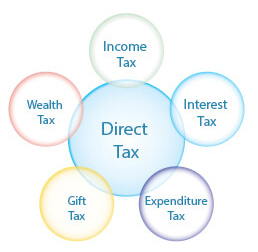
1.) Direct Tax
Taxes that are paid directly by organizations or individuals to the imposing entity are the Direct Taxes. A taxpayer pays direct taxes to the government based on different factors like; real estate property tax, personal property tax, income tax and taxes levied on assets.
Direct taxes differ entirely from indirect taxes because with indirect taxes the taxes levied on the service provider or the seller is transferrable to be paid by another. With direct tax, the imposed tax cannot be transferred to another individual or entity. The taxpayer upon whom the tax is levied is solely responsible for fulfilling the tax payment.
Direct Tax Levied as Income Tax
Taxes which are imposed by the government on financial earnings are called Income Tax. The law requires that any business or individual must file income tax return, every year to determine for unpaid dues and to know if one is eligible for a tax refund. Income tax makes up for a huge source of funds that the government utilizes for public service oriented projects. Many countries around the world employ a progressive income tax system where the higher income earners are required to pay a higher tax rate compared to the lower earners.
Direct Tax Levied as Corporate Tax
Corporate Tax is the taxes imposed on the income or gains generated by corporations. Generally, this tax is levied on the earnings of profits where the companies or business establishments are taxed as per the provision Income Tax rules.
Direct Tax Levied as Inheritance Tax
Inheritance Tax is also known as Estate Tax or Death Duty where taxes are imposed on the total value of the property, upon the death of the individual who owned the estate.
Direct Tax Levied as Gift Tax
When an individual receives a taxable gift then the tax imposed against the gift item must be paid to the government.
Determining Capital Gains Tax in India – Proceedings and Calculation Get Details
Benefits of Direct Taxation
There are various benefits that are applicable for Direct Taxation
Equitable
In Direct Taxation, the burden of the levied taxes can’t be transferred. It gives fair obligation of the taxes to be paid only on one’s income and wealth, thereby a consistent taxation system is achieved from all sections of a society.
Economical
All Income Tax and many other types of Direct Taxation are completed at a source with the process of TDS (Tax Deduction at Source) which allows the government to easily collect the taxes.
Certainty
It provides a sense of security and certainty as both the taxpayer and the government are aware of the tax amount to be paid.
Productivity
Direct taxes bring in a huge revenue to the government because the Indian working population is consistently growing and with the growth in the number of taxpayers, the returns from Direct Taxation also multiplies.
Creates Public Consciousness
Direct Taxation is educationally valuable as the taxpayer becomes aware of the burden of tax payment and eventually pays more interest towards how the government utilizes the public funds. The taxpayer also gain more education about the rights and responsibility of a citizen.
Creates Equal Distribution of Wealth
The government of India typically charges more taxes from the higher earners, equalizing the burden of every segment of taxpayers.
Relatively Elastic
The direct taxes are comparatively flexible because when there is an increase in income and wealth of individuals and companies, the return from direct taxes will also increase. This also implies that the government's fund can be expanded by elevating the rates of taxation.
Anti-inflationary
Direct taxes can help in regulating inflation. The government may increase Tax Rates during inflationary periods as a result, the expenditure demand may decline, which in turn may reduce inflation.
2.) Indirect Tax
An indirect tax is collected by an intermediary, from the consumer who is burdened with the financial liability of paying the taxes. Usually, indirect taxes increase the price of services and goods purchased by the consumer. Consumers are the segment who end up paying the taxes on the service renderers and goods manufacturers, by paying higher rates for the products.
Indirect Tax Levied as Service Tax
Service tax is a component of Central Excise where except for the state of Jammu and Kashmir, taxes are levied on services provided in India. The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) is the department responsible for collecting Service Tax. Service Tax is imposed indirectly on all the taxable services rendered by the service provider to its customer. The purpose of Service Tax is to reduce the intensity of taxation upon manufacturers and service providers without compelling the government to compromise on revenue needs.
Indirect Tax Levied as Excise Duty
For all the goods and commodities manufactured in India, a Central Excise Duty is imposed indirectly under The Central Excise Act, 1944. When a commodity is handed over from the manufacturer to a buyer, the tax is compounded by the manufacturer with the cost of goods and levied upon the buyer.
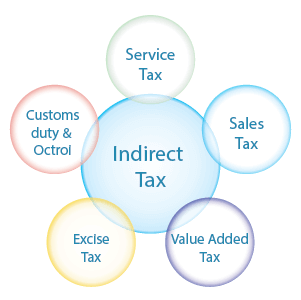
Indirect Tax Levied as VAT
Value Added Taxes are levied on the on movable goods and it is a collective taxation system where additional taxes are levied upon each step of the transaction in production or distribution chain. The consumers are ultimately the ones burdened with paying for this tax too.
What are the various factors in which the central government levies taxes upon?
The Central Government can levy taxes on factors like
- Income Tax Tax charged on the income of a person.
- Customs duties Duties imposed on import and export of goods.
- Central excise Taxes charged for the manufacturing of liable goods.
- Service tax Taxes levied for the provision of services.
Deciphering the Taxes, Charges and VAT on Restaurant Bills in India Get Details
What are the various factors in which the state government levies taxes upon?
The State Government can levy taxes on factors like
- Value Added Tax (VAT) Value Added Taxes are taxes imposed on the sale of goods. Intra-state (existing or occurring within the boundaries of a state) transactions of goods are covered by the VAT Law of that state, on the other hand, inter-state (existing or carried on between states) transactions are covered by the Central Sales Tax Act. The revenues collected under Central Sales Tax Act are also carried out by the State Government.
- Stamp Duties and Land Revenue Land Revenues are governed by the State Governments so, Stamp Duties on the transfer of stable properties are imposed by the State Governments.
- State Excise Excise duties are imposed on Liquor and certain agricultural goods.
Aside from the taxes imposed by the State and Central Government, certain taxation entitlement has been delegated in the hands of the local municipal bodies. The local governing bodies have the right to charge taxes on water, property, shop, establishment etc.
Read More About
People Also Searched For
Frequently Asked Questions
In the News
-
Save money with this special app to file your Income Tax Returns
Oneindia Hindi: Remember the days when doing taxes was a yearly ordeal that you would rather pay an accountant to deal with? Technology has made sure that that is no longer the case. Check out All India ITR’s newly launched e-filing app that lets you file your tax returns even while you’re on the go.
14th June 2017
Oneindia Hindi
 Tax
Tax
 Income Tax
Income Tax
 Sales Tax
Sales Tax
 TDS
TDS
 GST
GST
 Service Tax
Service Tax
 VAT
VAT
 Tax Calculator
Tax Calculator